Tipitaka >> Abhidhamma Pitaka >> Dhatukatha >> Chapter 3
Pali Versions : Pali-English Version and Pali-Devanagri Version
Translated by : U Narada
Chapter 3 : Unclassified and Classified[]
12 QUESTIONS AND ANSWERS
179. Feeling aggregate is not classified with these states ;
Perception aggregate ; Mental formation aggregate ; Origin truth ; Path
truth is not classified with these states under the same aggregate,
but classified under the same base and under the same element.
Under how many aggregates, under how many bases and under
how many elements are those states classified ? They, excluding
Nibbana from the classification of aggregates, are classified under
3 aggregates, under 1 base and under 1 element (5).
180. . . . Cessation truth is not classified with these states under
the same aggregate, but classified under the same base and under
the same element. . . . They are classified under 4 aggregates,
under 1 base and under 1 element (1).
181. . . . Life faculty is not classified with these states under the
same aggregate, but classified under the same base and under the
same element. . . . They, excluding Nibbana from the classification
o f aggregates, are classified under 2 aggregates, under 1 base and
under 1 element (1).
182. Female faculty is not classified with these states; Male
faculty ; Bodily pleasure faculty ; Bodily pain faculty ; Mental
joy faculty ; Grief faculty ; Indifference faculty ; Faith faculty ;
Energy faculty ; Mindfulness faculty ; Concentration faculty ;
Wisdom faculty ; I-shall-know-what-I-did-not-know faculty ; Higher
realization faculty; He-who-has-known faculty; Ignorance ;
Conditioned by ignorance, Formations; Conditioned by 6 bases.
Contact; Conditioned by contact, Feeling ; Conditioned by feeling.
Craving ; conditioned by craving, Clinging ; Kamma becoming is
not classified with these states under the same aggregate, but
classified under the same base and under the same element.. . . They,
excluding Nibbana from the classification of aggregates, are classified
under 3 aggregates, under 1 base and under 1 element (22).
183. Birth ; Ageing ; Death ; Jhana is not classified with these
states under the same aggregate, but classified under the same base
and under the same element. . . . They, excluding Nibbana from the
classification of aggregates, are classified under 2 aggregates, under
1 base and under 1 element (4).
184. Sorrow ; Suffering ; Grief; Despair ; Application of mindfulness ;
Great effort; lllimitables ; 5 Faculties ; 5 Strengths ;
7 Factors of Enlightenment; Noble Eightfold Path ; Contact;
Feeling; Perception; Volition; Decision ; Attention ; States
which are roots; States which are roots and also have associated
roots ; States which are roots and also associated with roots are not
classified with these states under the same aggregate, but classified
under the same base and under the same element They, excluding
Nibbana from the classification of aggregates, are classified under
3 aggregates, under 1 base and under 1 element (20).
185. States not arising from 4 causes ; States not conditioned by
4 causes are not classified with these states under the same aggre gate,
but classified under the same base and under the same element.
. . . They are classified under 4 aggregates, under 1 base and under
1 element (2).
186. States which are cankers ; States which are both cankers
and objects of cankers ; States which are both cankers and associated
with cankers are not classified with these states under the same
aggregate, but classified under the same base and under the same
element. . . . They, excluding Nibbana from the classification of
aggregates, are classified under 3 aggregates, under 1 base and under
1 element (3).
187. Fetters . . . Ties . . . Floods . . . Bonds . . . Hindrances . . .
States which are misapprehensions; States which are both misapprehensions
and objects of misapprehensions are not classified
with these states under the same aggregate, but classified under
the same base and under the same element. . . . They, excluding
Nibbana from the classification of aggregates, are classified under
3 aggregates, under 1 base and under 1 element (17).
188. States which are mental factors ; States which are associated
with consciousness ; States which are conjoined with consciousness ;
States which are conjoined with and are generated by conscious ness ;
States which are conjoined with, are generated by and arise
together with consciousness ; States which are conjoined with, are
generated by and arise successively with consciousness are not
classified with these states under the same aggregate, but classified
under the same base and under the same element They, excluding
Nibbana from the classification of aggregates, are classified under
1 aggregate, under 1 base and under 1 element (6).
189. States which arise together with consciousness ; States which
arise successively with consciousness are not classified with these
states under the same aggregate, but classified under the same base
and under the same element. . . . They are not classified under any
aggregates ; they are classified under 1 base and under 1 element (2).
190. States which are clinging. . . . States which are corruptions;
States which are both corruptions and objects of corruptions;
States which are both corruptions and corrupt; States which are
both corruptions and associated with corruptions are not classified
with these states under the same aggregate, but classified under the
same base and under the same element.
Under how many aggregates, under how many bases and under
how many elements are those states classified ? They, excluding
Nibbana from the classification of aggregates, are classified under
3 aggregates, under 1 base and under 1 element (7).
Mnemonic
Three aggregates, likewise truths, sixteen faculties.
Fourteen dependent originations, next fourteen.
Thirty kinds belonging to ten clusters.
Two kinds from lesser couplets, eight kinds from intermediate
couplets.
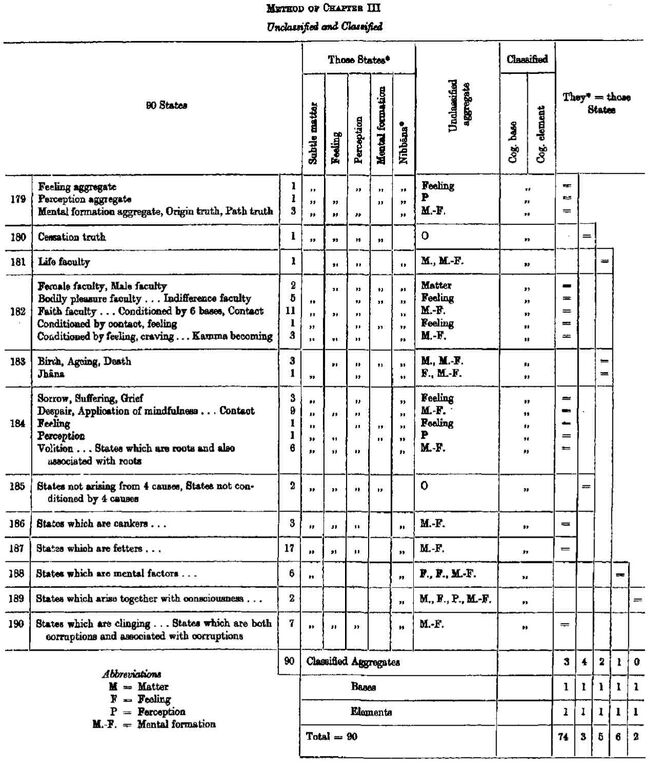
Explanation of the Method and Chart of Chapter III
Subject Matter : 90 states that come under cognizable base, i.e.
subtle matter, feeling, perception, mental formation and Nibbana,
form the subject matter of this chapter. These are the states which
can be classified under the same base and under the same element
but not under the same aggregate. All the remaining states of the
Text are excluded because they include gross matter and consciousness.
The former comes under different bases and different elements
while the latter comes under different elements. Out of these
90 states, 50 belong to the internal and 40 to the external states of
enquiry.
Questions and Answers : There are 12 sets of questions and
answers, Nos. 179-190
“ These States ” : The rules for determining “ these states ” are
as follows :-
1. When the subject of enquiry belongs to one of the 5 states,
namely; subtle matter, feeling, perception, mental formation and
Nibbana, that come under cognizable base, the remaining 4 states
are taken as “ these states. Since these 5 states come under
different aggregates they cannot be classified under the same aggre gates.
But they come under cognizable base and under cognizable
element and, therefore, they can be classified under the same base
and under the same element. For example, when feeling aggregate
is dealt with, the remaining 4 states, subtle matter, perception,
mental formation and Nibbana are taken as “ these states ” . The
feeling aggregate comes under feeling aggregate and the remaining
4 states come under different aggregates and so they cannot be
classified under the same aggregate. But feeling aggregate comes
under cognizable base and under cognizable element and so do the
remaining 4 states. Thus they can be classified under the same base
and under the same element.
The case where, like the feeling aggregate in No. 179, the remaining
4 states are taken as “ these states ” applies also to Nos. 180, 182,
184, 185, 186, 187 and 190. 77 states of enquiry are dealt with in
this case. In Nos. 180 and 185, where Nibbana is the state of
enquiry, it must be remembered that Nibbana is excluded from the
classification of aggregates.
2. When the subject of enquiry belongs to 2 out of the 5 states
under cognizable base, the remaining 3 states are taken as “ these
states ” . This is the case with Nos. 181 and 183 where 5 states of
enquiry are dealt with.
Life faculty in No. 181 consists of both physical and psychical
life, the former comes under subtle matter and the latter under
mental formation. So the remaining 3 states, feeling, perception and
Nibbana are taken as “ these states ” .
Birth, Ageing and Death in No. 183 refer to both materiality and
mentality where the former comes under subtle matter and the
latter under mental formation and so “ these states ” are the same
as in life-faculty above.
Jhana in No. 183 consists of applied-thought, sustained-thought,
rapture, bliss and one-pointedness of mind. Bliss is feeling and the
rest are mental formations. So the remaining 3 states, subtle matter,
perception and Nibbana are taken as “ these states ” .
3. When the subject of enquiry belongs to 3 of the 5 states under
cognizable base, the remaining 2 states are taken as “ these states".
This is the case with No. 188 where 6 states of enquiry are dealt
with. They are all mental factors, i.e. feeling, perception and
mental formation. So the remaining 2 states, subtle matter and
Nibbana, are taken as “ these states ” .
4. When the subject of enquiry belongs to 4 of the 5 states under
cognizable base, the remaining state is taken as “ these states ” .
This is the case with No. 189 where 2 states of enquiry are dealt
with. Each consists of 52 mental factors and 2 intimations, the
former coming under feeling, perception and mental formation and
the latter under subtle matter. So the only remaining state, Nibbana,
is taken as these states ” .
“ Those States ” : “ Those states ” are the same as the states
that were taken for “ these states ” . This is shown by the sign of
equality in the column.
Classified: The aggregates included in “ those states ” can be
read off from those given in the corresponding “ these states ” for
the purpose of classification under the aggregates, bases and elements.
Wherever Nibbana is included in “ those states ” it is excluded
from the classification under the aggregate. As regards classification
under bases and elements, it is always the same, namely : cognizable
base and cognizable element. In the case of No. 189, the zero in the
classified aggregates table indicates that Nibbana is excluded from
the classification. This is similarly shown in the unclassified
aggre gates column with Nos. 180 and 185, the states of enquiry being
Nibbana.
How to read the Chart: Take the feeling aggregate as an illustra tion.
Feeling aggregate is not classified with these states (subtle
matter, perception, mental formation and Nibbana) under the same
aggregate (feeling aggregate) but classified under the same base
(cognizable base) and under the same element (cognizable element).
Under how many aggregates, under how many bases and under
bow many elements are those states (subtle matter, perception,
mental formation and Nibbana) classified ? They, excluding Nibbana
from the classification of aggregates, are classified under 3 aggregates
(matter, perception and mental formation aggregates), under 1 base
(cognizable base) and under 1 element (cognizable element).
The kinds of “ those states ” (or “ these states ” ) : On examina tion
of the columns of “ those states ” it is found that there are
9 kinds of “ those states". The numbers of the states of enquiry
which give the same kind are shown in brackets along with the
questions. This can be found from the column of “ these states".
|
Question Numbers |
No. of States |
|
1. 179 (1), 182 (6), 184 (4) |
11 |
|
2. 179 (1), 184 (1) |
2 |
|
3. 179 (3), 182 (14), 184 (15), 186 (3), 187 (17), 190 (7) |
59
|
|
4. 180 (1), 185 (2) |
3 |
|
5. 181 (1), 183 (3) |
4 |
|
6. 182 (2) |
2 |
|
7. 183(1) |
1 |
|
8. 188 (6) |
6 |
|
9. 189(2) |
2 |
|
|
Total 90 |
The kinds of Answers : The classified table below the chart shows
that there are 5 kinds of answers. The same answer is given by a
number of “ those states The numbers of the states of enquiry
which give the same kind can be read off from the chart.
|
Answers |
Question Numbers |
No. of States |
|
(1) 3, 1, 1 |
179 (5), 182 (22), 184 (20), 186 (3), 187 (17), 190 (7) |
74 |
|
(2) 4, 1, 1 |
180 (1), 185 (2) |
3
|
|
(3) 2, 1, 1 |
181 (1), 183 (4) |
5
|
|
(4) 1, 1, 1 |
188 (6) |
6
|
|
(5) 0, 1, 1 |
189 (2) |
2 |
|
|
|
Total 90
|
The kinds of aggregates, bases and elements corresponding to
the numbers can be found out from the corresponding column of
“ these states ” . They are the same as “ those states".